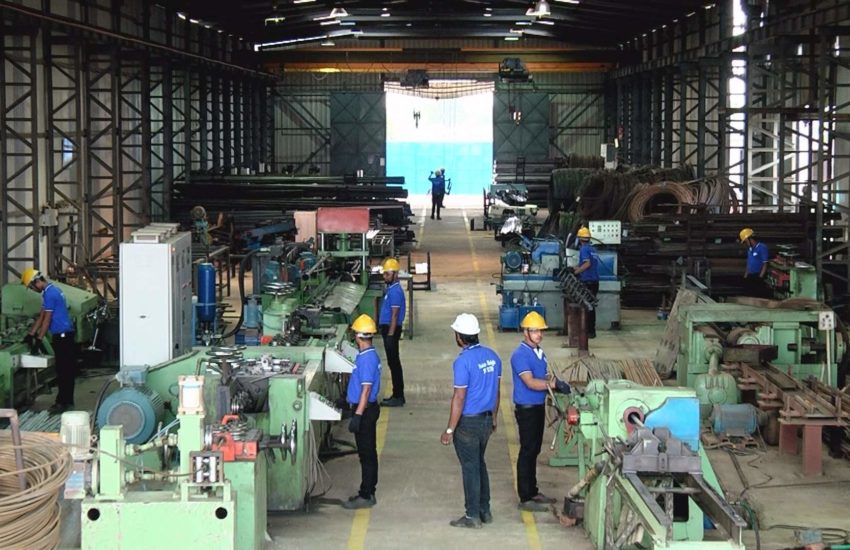
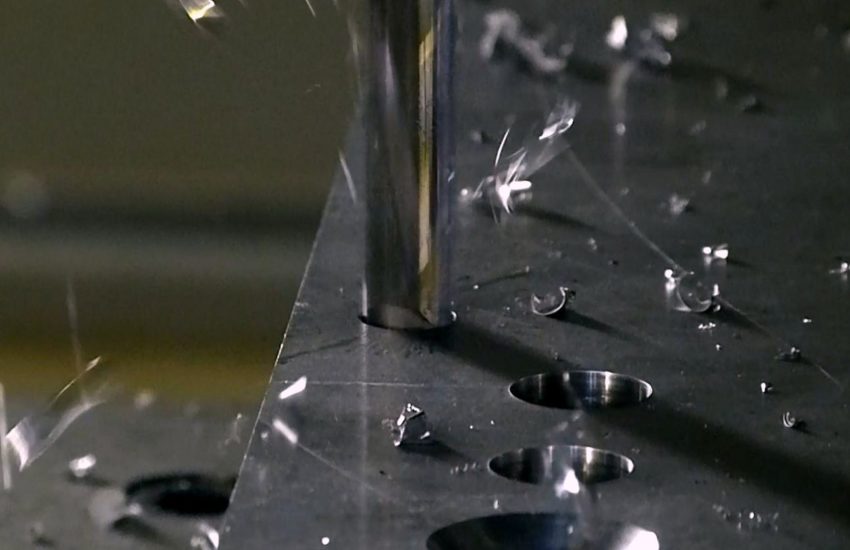
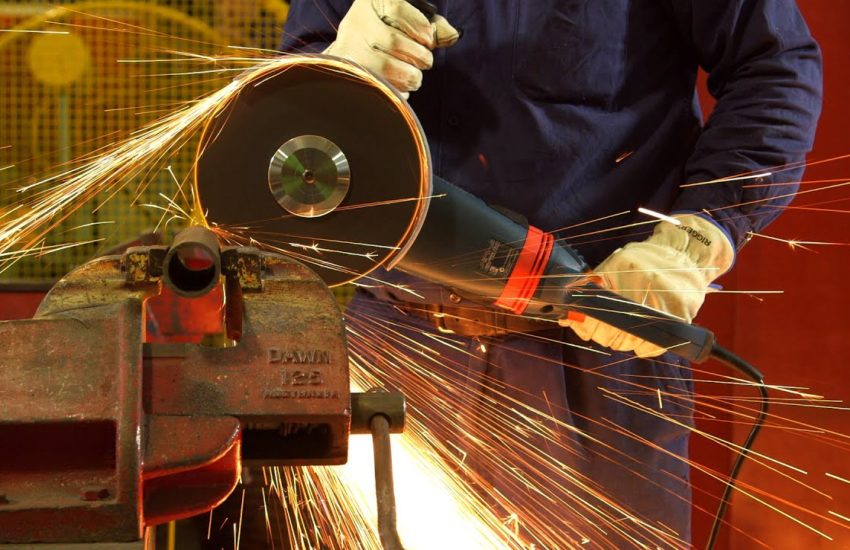
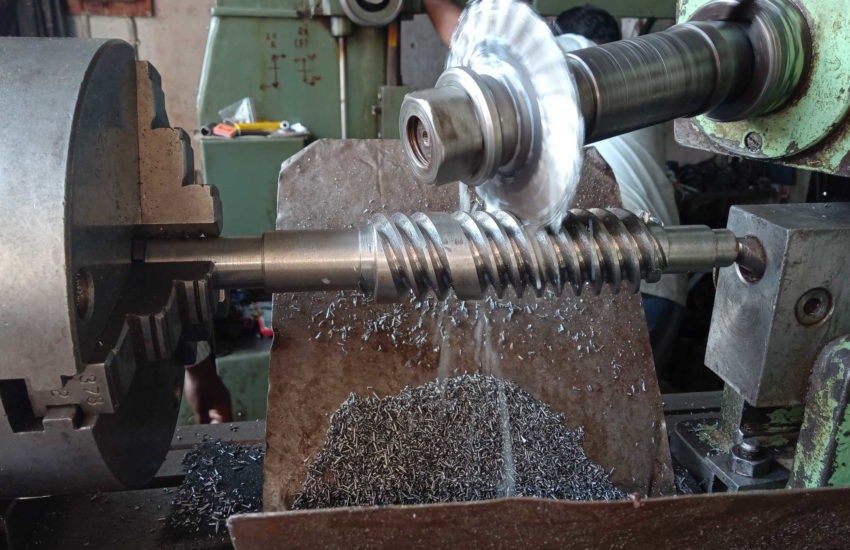
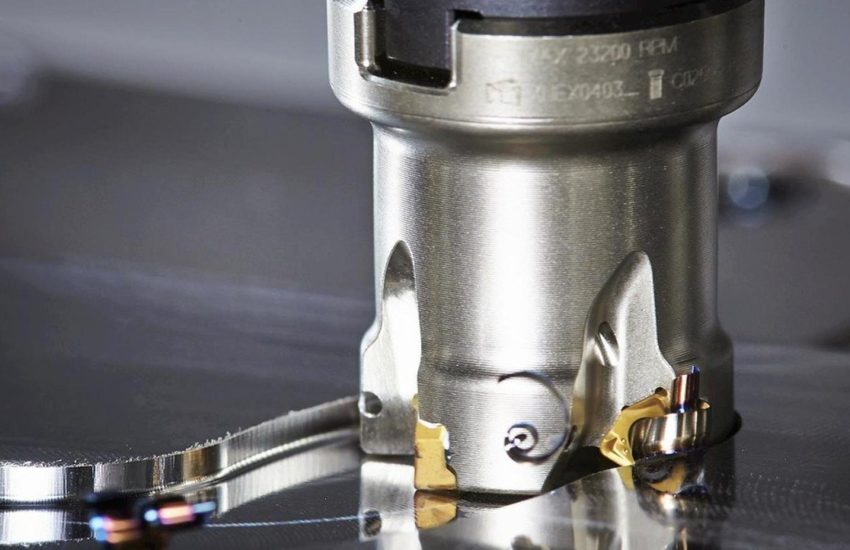
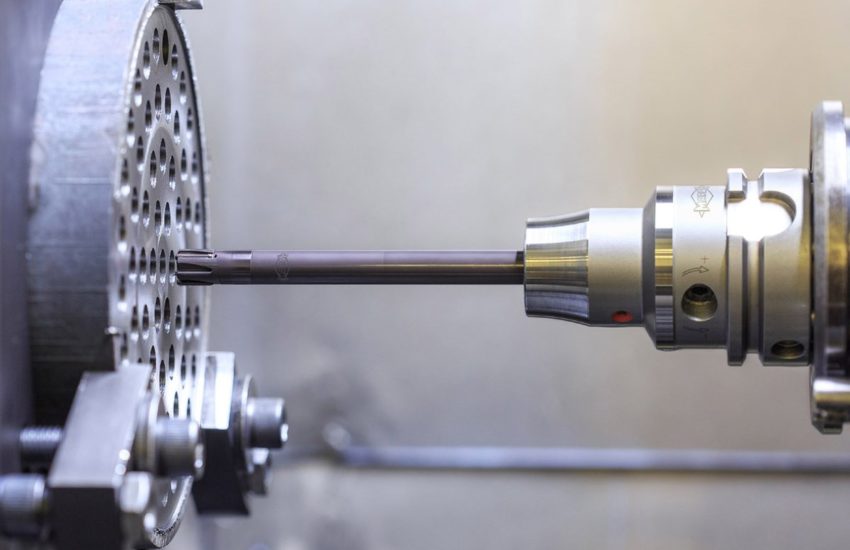
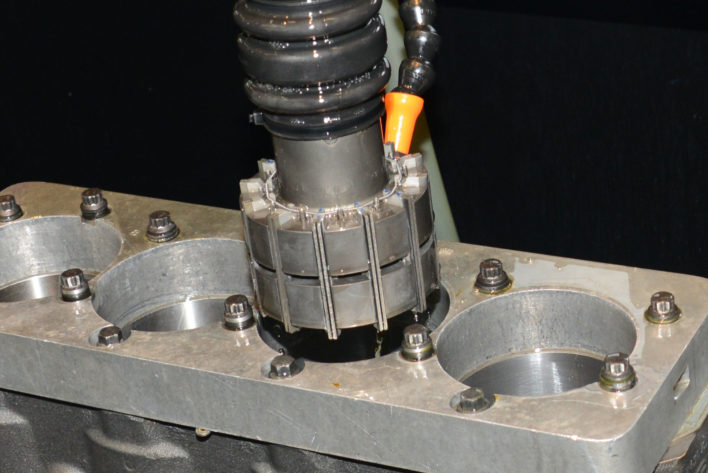
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining is a high-precision and automated manufacturing process that utilizes pre-programmed software to control machine tools. This process allows for the precise cutting, shaping, and drilling of materials with minimal human intervention, ensuring accuracy and repeatability. CNC machining is widely used across industries requiring complex geometries, tight tolerances, and superior finishes.
One of the biggest advantages of CNC machining is its efficiency. Unlike manual machining, CNC machines operate continuously with minimal downtime, increasing production rates while maintaining consistency. The process also allows for rapid prototyping and mass production without compromising quality. Additionally, CNC machining is highly adaptable, capable of handling a variety of materials such as metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
CNC machining is a vital component in modern manufacturing, supporting industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics. By leveraging automation and precision engineering, CNC machining enables the production of complex components with extreme accuracy, enhancing the reliability and performance of end products.
Key Features:
High precision and repeatability.
Ensures consistent quality and accuracy in manufacturing.
Compatible with a wide range of materials.
Works with metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
Reduces manual labor and operational costs.
Automates processes for higher efficiency and cost savings.
Ideal for both prototyping and mass production.
Supports rapid development and large-scale manufacturing.
Common Applications:
Aerospace and automotive components.
Used for lightweight, high-strength parts with tight tolerances.
Custom prototypes and tooling.
Enables rapid design iterations and specialized manufacturing.
Medical implants and electronic enclosures.
Provides biocompatible, precision-engineered solutions.
Our Sub-Services Includes.
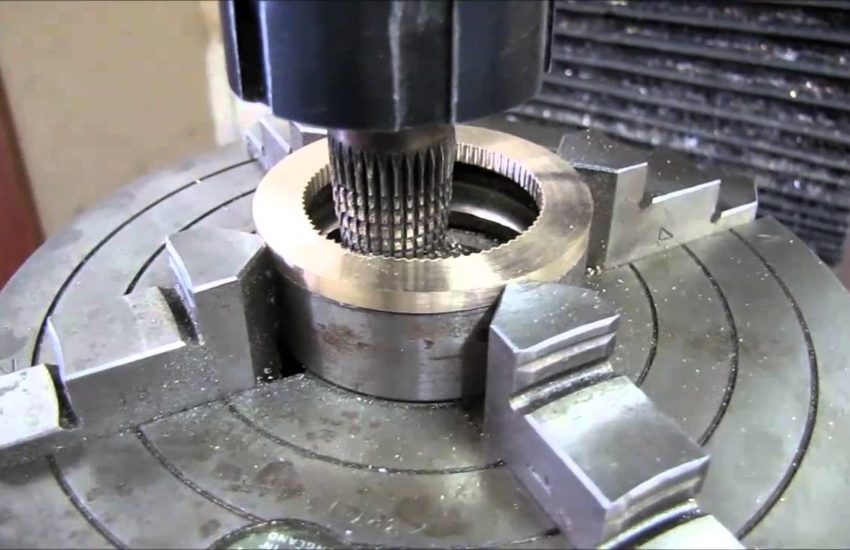

Broaching
Got questions or need assistance with your Industry needs?

Buffing
Polishing and buffing are finishing processes for smoothing a workpiece’s surface using an abrasive and a work wheel.
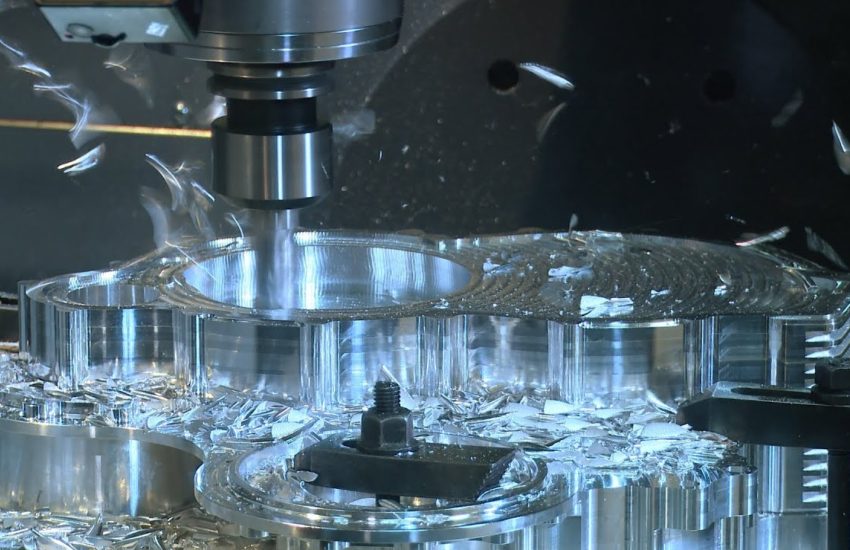

CNC & VMC Machining
It is a subtractive manufacturing process which typically employs computerized controls and machine tools.
Drilling
For hard metals such as stainless steel, it’s best to use drill bits made of chrome vanadium, cobalt or titanium carbide.
Grinding
Metal Grinding is used to finish off rough edges, deburr metal parts, smooth welds, create sharp edges.
Groove Cutting
In manufacturing or mechanical engineering a groove is a long and narrow indentation built into a material
Hobbing
Hobbing is a machining process for gear cutting, cutting splines, and cutting sprockets on a hobbing machine Read More
Honing
It is a process that produces a precision surface on a metal workpiece by scrubbing an abrasive stone against it.
Lapping
It is a controlled polishing process between two surfaces that are rubbed together to create an accurate finish on a part. Read More
Milling
Milling is a cutting process that uses a milling cutter to remove material from the surface of a workpiece Read More
Reaming
Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount with high degree of accuracy
Shaping/ Forming
It is the metalworking process of fashioning metal parts and objects through mechanical deformation
Tapping
The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.
Turning
Turning is used to reduce the diameter of the work piece, usually to a specified dimension, and to produce a smooth finish. Read More