Surface Protection Treatment involves applying coatings, sealants, and treatments to materials to enhance their resistance against environmental factors such as corrosion, wear, and UV exposure. This process is essential for extending the lifespan of components and ensuring that they perform reliably under harsh conditions.
There are various types of surface protection treatments, including powder coating, anodizing, electroplating, and galvanizing. These methods not only improve durability but also enhance the appearance of the final product. Advanced techniques such as nanocoatings and polymer-based protective films are also gaining popularity in precision industries.
Industries such as construction, marine, oil & gas, and electronics extensively use surface protection treatments to safeguard their products. These treatments help reduce maintenance costs and prevent material degradation, making them a vital part of the manufacturing and engineering sectors.
Key Features
- Provides enhanced corrosion and wear resistance.
- Improves surface aesthetics and durability.
- Reduces maintenance costs and extends product life.
Common Applications
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for industrial equipment and pipelines.
- Protective treatments for automotive and aerospace components.
- UV and chemical-resistant coatings for electronic devices.
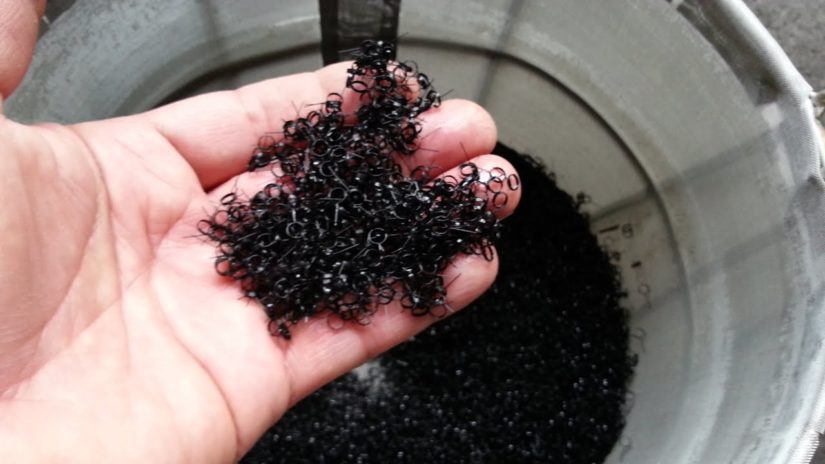

Blackodizing (Black Oxide)
Black oxide or blackening is a conversion coating for ferrous materials, stainless steel, copper and copper based alloys etc
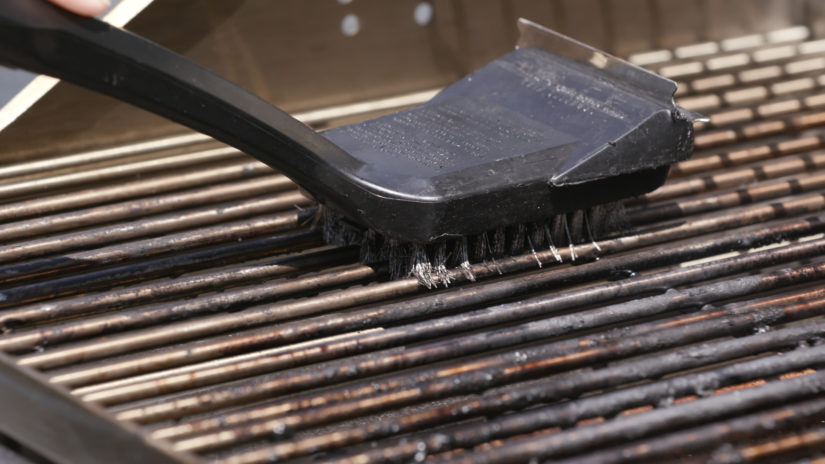

Brushing
It is produced by polishing the metal with a 120–180 grit belt or wheel then softening with an 80–120 grit greaseless compound

Dipping
Also known as hydro dipping or cubic printing, is a method of applying printed designs to three-dimensional surface
Electroplating
It is a process that uses an electric current to reduce dissolved metal cations so that they form a thin coherent metal coating.
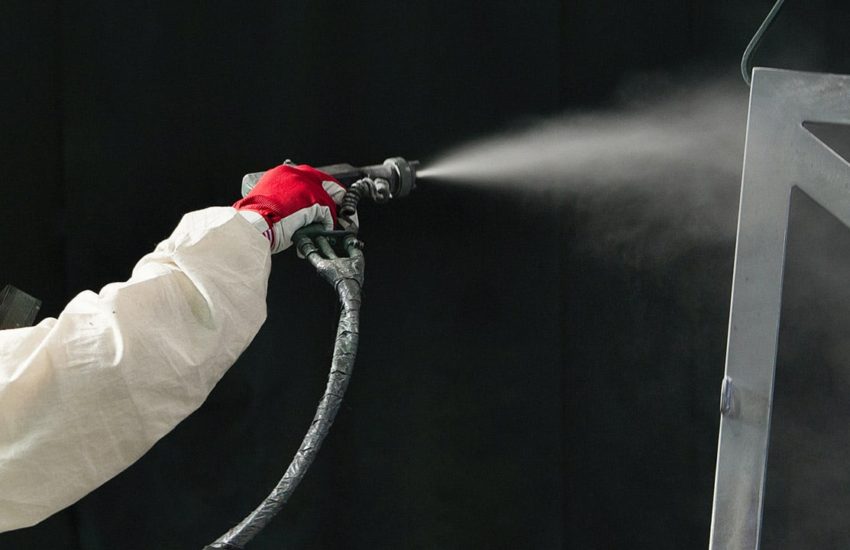
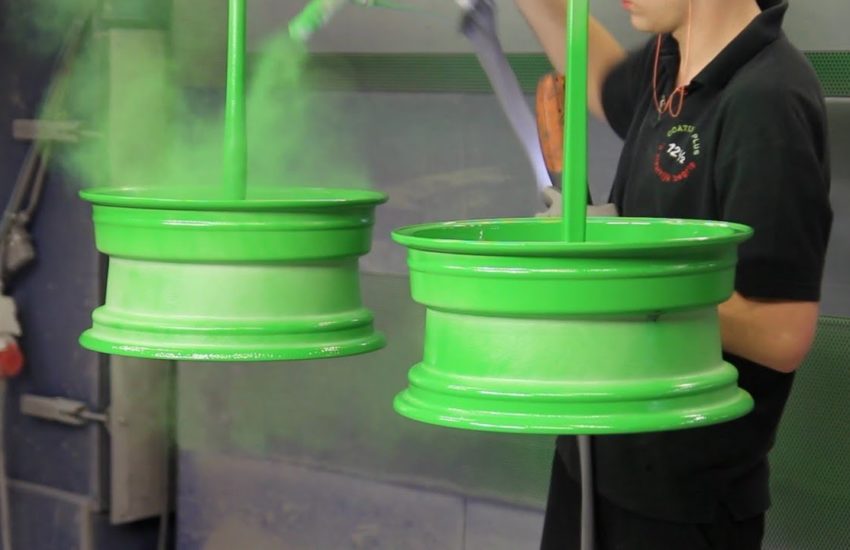
Electrostatic Painting
Electrostatic painting defines a paint application technique that is based on the concept that opposites attract
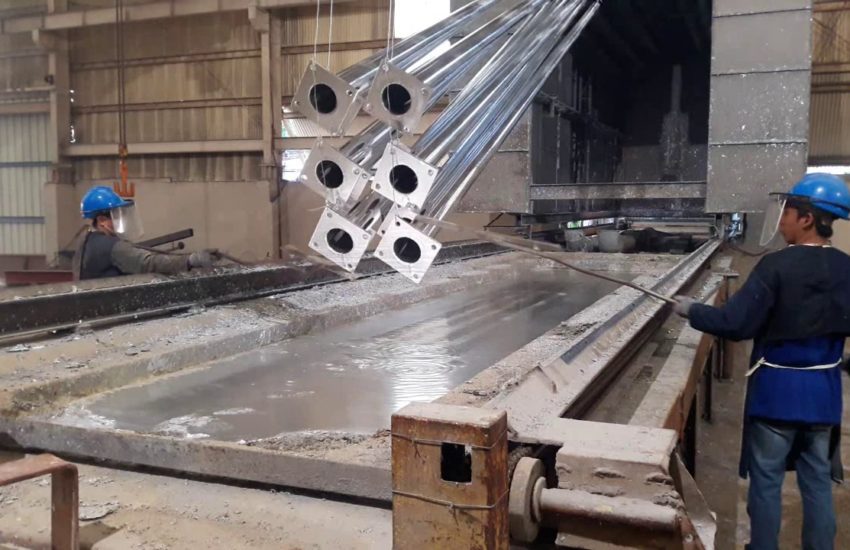
Hot Dip Galvanizing
When clean steel is immersed into molten zinc, a series of zinc-iron alloy layers are formed by a metallurgical reaction
Lamination
The electrical equipment such as transformers and motors usually use a steel laminate to form the core of the coils.
Passivation
Passivation is the process of treating or coating a metal in order to reduce the chemical reactivity of its surface.
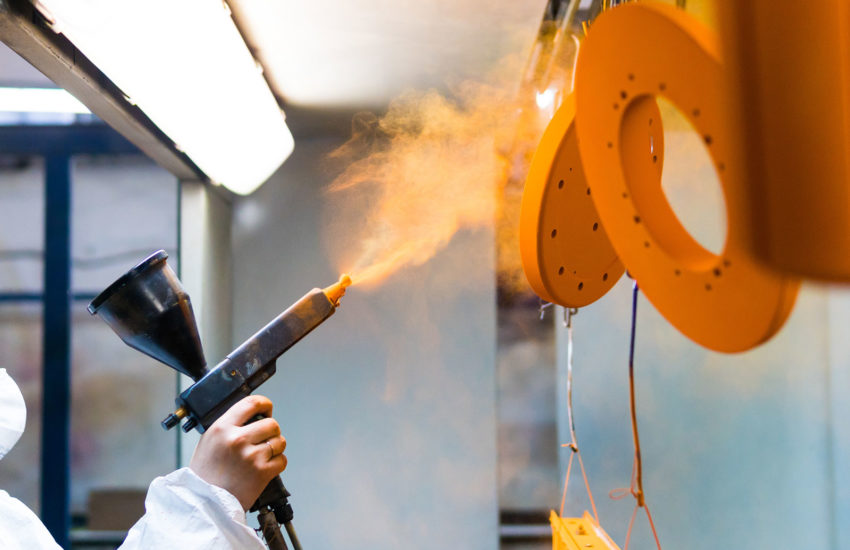
Power Coating
Powder may be thermoplastic or thermoset polymer. It is used to create a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint
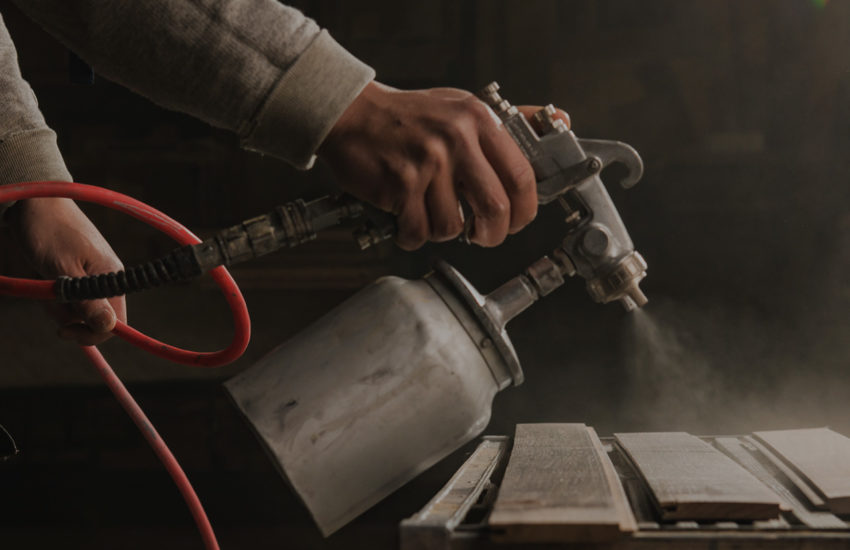
Spray Painting
Priming metal is important, as metal primer spray provides a surface that regular spray paint can then bond to.